Graphical Representation of Motion
Graphical Representation of Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as, Displacement - Time Graphs, Distance - Time Graphs, Velocity - Time Graphs & Velocity - Time Graphs with Discontinuities etc.
Important Questions on Graphical Representation of Motion
The velocity-time graph of the particle moving along a straight line is shown. The rate of acceleration and deceleration is constant and it is equal to . If average velocity during the motion is , then find the value of
The shape of a distance-time graph for constant accelerated motion moving in a single direction is
A ball is dropped from a certain height on the surface of the glass. It collides elastically and comes back to the initial position. If this process is repeated then the velocity-time graph is:-
A ball is dropped from some height. After rebounding from the floor it ascends to the same height. Draw the velocity-time graph for the given motion.
A batsman hits a sixer and the ball touches the ground outside the cricket ground. Among the following graph, the one that describes the variation of the cricket ball's vertical velocity with time between the time as it hits the bat and time when it touches the ground is
If the height can be expressed as , the value of after is
In projectile motion, the height of the object varies with respect to time.
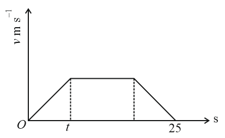
The speed of a train increases at a constant rate from zero to and then remains constant for an interval and finally decreases to zero at a constant rate . The total distance travelled by the train is . The time taken to complete the journey is . Then,
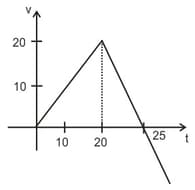
The fig. shows the v-t graph of a particle moving in straight line. Find the time (in seconds) when particle returns to the starting point.
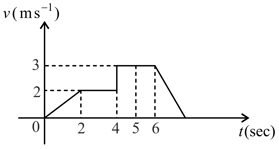
For given graph find out displacement from to second
The acceleration -time graph of a body is shown below.
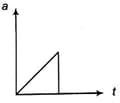
The most probable velocity-time graph of the body is
The velocity - time graph of a body is shown in figure. The ratio of the ...during the intervals OA and AB is .... 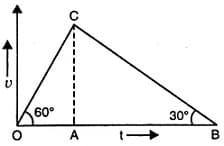
A rocket is fired upwards. Its fuel exhausts fully in 12 seconds. The height reached by the rocket as calculated from its velocity-time graph is
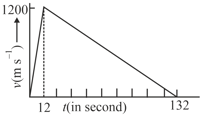
The velocity-time graph of a particle moving along a straight line is shown in the figure. The displacement of the body in is
The displacement-time graphs of two particles and are straight lines making angles of respectively and with the time axis. If the velocity of is and that of is , then the value of is
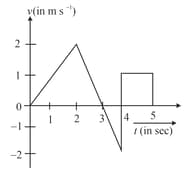
The variation of velocity of a particle moving along a straight line is shown in the figure. The distance travelled by the particle in is
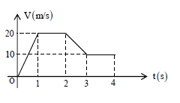
The velocity-time graph of a particle moving along a straight line is as shown in diagram. The rate of acceleration and retardation is constant and is equal to . If the average velocity during the motion is , then
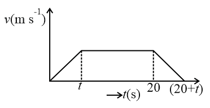
The distance travelled with uniform velocity is
shows the velocity (v) of a particle plotted against time (t).
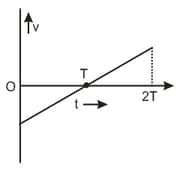
Initially car is ahead of car . Both start moving at time in the same direction along a straight line. The velocity time graph of two cars is shown in figure. The time when the car will catch the car , will be ;
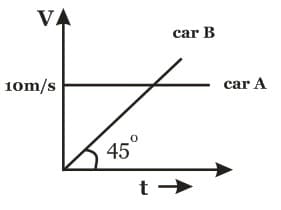
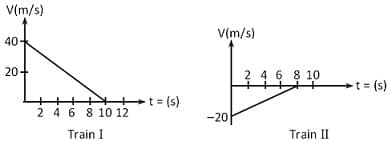
Two trains, which are moving along different tracks in opposite directions, are put on the same track due to a mistake. Their drivers, on noticing the mistake, start slowing down the trains when they are 300 m apart. Graphs given below show their velocities as a function of time as they slow down. The separation between the trains, when both have stopped, is :